Graphing in Python with Matplotlib
Video Lectures
Displaying all 32 video lectures.
Lecture 1 Play Video |
Introduction and Line Welcome to a Matplotlib with Python 3+ tutorial series. In this series, we're going to be covering most aspects to the Matplotlib data visualization module. Matplotlib is capable of creating most kinds of charts, like line graphs, scatter plots, bar charts, pie charts, stack plots, 3D graphs, and geographic map graphs. First, in order to actually use Matplotlib, we're going to need it! If you have a later version of Python installed, you should be able to open cmd.exe/terminal and then run: pip install matplotlib Note: You may need to do C:/Python34/Scripts/pip install matplotlib if the above shorter version doesn't work. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 2 Play Video |
Legends titles and labels In this tutorial, we're going to cover legends, titles, and labels within Matplotlib. A lot of times, graphs can be self-explanatory, but having a title to the graph, labels on the axis, and a legend that explains what each line is can be necessary. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 3 Play Video |
bar charts and histograms The plt.bar creates the bar chart for us. If you do not explicitly choose a color, then, despite doing multiple plots, all bars will look the same. This gives us a change to cover a new Matplotlib customization option, however. You can use color to color just about any kind of plot, using colors like g for green, b for blue, r for red, and so on. You can also use hex color codes, like #191970 Next, we can cover histograms. Very much like a bar chart, histograms tend to show distribution by grouping segments together. Examples of this might be age groups, or scores on a test. Rather than showing every single age a group might be, maybe you just show people from 20-25, 25-30... and so on. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 4 Play Video |
Scatter Plots Next up, we cover scatter plots! The idea of scatter plots is usually to compare two variables, or three if you are plotting in 3 dimensions, looking for correlation or groups. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 5 Play Video |
stack plots In this Matplotlib data visualization tutorial, we cover how to create stack plots. The idea of stack plots is to show "parts to the whole" over time. A stack plot is basically like a pie-chart, only over time. Let's consider a situation where we have 24 hours in a day, and we'd like to see how we're spending out time. We'll divide our activities into: Sleeping, eating, working, and playing. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 6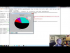 Play Video |
Pie Charts Pie charts are a lot like the stack plots, only they are for a certain point in time. Typically, a Pie Chart is used to show parts to the whole, and often a % share. Luckily for us, Matplotlib handles the sizes of the slices and everything, we just feed it the numbers. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 7 Play Video |
loading data from files Many times, people want to graph data from a file. There are many types of files, and many ways you may extract data from a file to graph it. Here, we'll show a couple of ways one might do this. First, we'll use the built-in csv module to load CSV files, then we'll show how to utilize NumPy, which is a third-party module, to load files. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 8 Play Video |
getting data from the internet Aside from loading data from the files, another popular source for data is the internet. We can load data from the internet from a variety of ways, but, for us, we're going to just simply read the source code of the website, then use simple splitting to separate the data. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 9 Play Video |
converting data from the internet This tutorial is focused around converting the datestamps from the Yahoo finance API to times that Matplotlib understands. To do this, we're going to write a new function, bytespdate2num. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 10 Play Video |
basic customizations, rotating labels In this Matplotlib tutorial, we're going to be talking about some of the possible customizations to graphs. In order to start modifying the subplots, we have to define them. We will talk about them soon, but there are two major ways to define subplots, and to structure them. For now, we'll just use one of them, but we will be explaining them shortly. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 11 Play Video |
handling unix time In this Matplotlib tutorial video, we're going to cover how to handle the conversion of unix time stamps to then plot date stamps in your graph. With the Yahoo Finance API, you will notice that if you use large time frames, like 1y for one year, you will get those date stamps we've been working with, but, if you use something like 10d for 10 days, you will instead get timestamps that are unix time. Unix time is the number of seconds after Jan 1st 1970, and it represents a normalized method for time across programs. That said, Matplotlib doesn't want unix time stamps. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 12 Play Video |
more customization of colors and fills In this tutorial, we're going to cover some more customization, along the lines of colors and fills. Fills allow us to fill between points. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 13 Play Video |
spines and horizontal lines Welcome to another customization tutorial, where we discuss spines and horizontal lines with Matplotlib. Something you might want to do from time to time is to change the color of a spine, or maybe even remove one all together. A spine to a graph is basically the edge of the graph, where we have the ticks and such. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 14 Play Video |
candlestick OHLC graphs In this Matplotlib tutorial, we're going to cover how to create open, high, low, close (OHLC) candlestick charts within Matplotlib. These graphs are used to display time-series stock price information in a condensed form. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 15 Play Video |
styles In this Matplotlib tutorial, we're going to be talking about styles. With Matplotlib, we have styles which serve a very similar purpose to Matplotlib graphs as CSS (cascading style sheet) pages serve for HTML. As you can see up to this point, all of these changes we're making to our graphs start to add up, and we only have one axis so far! We could use for loops to at least keep the amount of code down, but we can also make use of these styles with Matplotlib. The idea of a style page is to write your customization to a style file, and then, to use those changes and apply them to your graph, all you do is import style and then use that specific style. This way, let's say you are finding yourself always changing various elements of your graphs. Instead of having to write 25-200 lines of customization code per chart, you can just write it once to a style, and then load in that style and apply all of those changes in two lines! Let's get started. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 16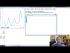 Play Video |
Live graphs In this Matplotlib tutorial, we're going to cover how to create live updating graphs that can update their plots live as the data-source updates. You may want to use this for something like graphing live stock pricing data, or maybe you have a sensor connected to your computer, and you want to display the live sensor data. To do this, we use the animation functionality with Matplotlib. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 17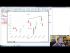 Play Video |
annotations and placing text In this tutorial, we're going to be talking about how we add text to Matplotlib graphs. We can do this in two ways. One is to just place text to a location on the graph. Another is to specifically annotate a plot on the chart to draw attention to it. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 18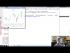 Play Video |
annotating last price to edge of matplotlib graph example In this Matplotlib tutorial, we're going to show an example of how we can track the last price of a stock, by annotating it to the right side of the axis like a lot of charting applications will do. While people like to see historical prices in their live graphs, they also want to see the most recent price. What most applications do, is the annotate the last price at the y-axis height of the price, and then kind of highlight it and move it around a bit in a box of sorts as price changes. Using our recently-learned annotation tutorial, we can do this along with adding a bbox. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 19 Play Video |
subplots In this Matplotlib tutorial, we're going to be discussion subplots. There are two major ways to handle for subplots, which are used to create multiple charts on the same figure. For now, we'll start with a clean slate of code. If you're following along linearly, then make sure to keep the old code on hand, or you can always revisit the previous tutorial for the code again. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 20 Play Video |
implementing subplots to our stock chart In this Matplotlib tutorial, we'll be handling our previous tutorial's code, and implementing the subplot configuration from the previous tutorial. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 21 Play Video |
adding more indicator data to our charts In this Matplotlib tutorial, we cover adding a couple simple functions to calculate data for us to fill our axis with. One is a simple moving average, the other is a simple high minus low calculation for prices. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 22 Play Video |
cleaning chart, custom fills, pruning Welcome to another Matplotlib tutorial! In this tutorial, we're going to clean our chart a bit, and then do a few more customizations. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 23 Play Video |
sharex axis In this tutorial for data visualization in Matplotlib, we're going to be talking about the sharex option, which allows us to share the x axis between plots. Sharex is maybe better thought of as "duplicate x." sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 24 Play Video |
multi y axis plotting volume on stock chart In this Matplotlib tutorial, we're going to cover how we can have multiple Y axis on the same subplot. In our case, we're interested in plotting stock price and volume on the same graph, and same subplot. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 25 Play Video |
customizing Matplotlib Legends In this Matplotlib tutorial, we're going to be going over custom legends. We've covered the basics of adding a legend already. The main issue with legends is typically that the legend gets in the way of data. There are a few options here. One option is to put the legend outside of the axis, but we have multiple subplots here and that would be pretty difficult. Instead, we'll make the legend a bit smaller, and then apply an alpha to it. First, to have a legend, we need to add labels to our data that we want to show up on the legend. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 26 Play Video |
Basemap intro In this Matplotlib tutorial, we're going to be covering the geographic plotting module, Basemap. Basemap is an extension to Matplotlib. In order to use Basemap, we first need it. To get Basemap, you can either get it from here: http://matplotlib.org/basemap/users/download.html, or you can go to http://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/. If you are having trouble installing Basemap, check out the pip installation tutorial. Once you have Basemap installed, you're ready to create maps. First, let's just project a simple map. To do this, we need to import Basemap, pyplot, create the projection, draw at least some sort of outline or data, then we can show the graph. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 27 Play Video |
Basemap customization options In this Matplotlib tutorial, we continue with the Basemap geographic plotting extension. We're going to show some of the customization options available to us. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 28 Play Video |
plotting coordinates on a map with Basemap Welcome to another Basemap with Matplotlib tutorial. In this tutorial, we're going to cover how to plot single coordinates, as well as how to connect those coordinates in your geographic plot. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 29 Play Video |
matplotlib 3d intro Hello and welcome to a 3D graphing in Matplotlib tutorial. Three dimensional graphing in Matplotlib is already built in, so we do not need to download anything more. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 30 Play Video |
3d scatter plot Welcome to another 3D Matplotlib tutorial, covering how to graph a 3D scatter plot. Graphing a 3D scatter plot is very similar to the typical scatter plot as well as the 3D wire_frame. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 31 Play Video |
3d bar charts In this Matplotlib tutorial, we cover the 3D bar chart. The 3D bar chart is quite unique, as it allows us to plot more than 3 dimensions. No, you cannot plot past the 3rd dimension, but you can plot more than 3 dimensions. With bars, you have the starting point of the bar, the height of the bar, and the width of the bar. With a 3D bar, you also get another choice, which is depth of the bar. Most of the time, a bar chart starts with the bar flat on an axis, but you can add another dimension by releasing this constraint as well. sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |
Lecture 32 Play Video |
conclusion Welcome to the final Matplotlib tutorial video. Here we will wrap up the series, and show a slightly more complex 3D wireframe sample code: http://pythonprogramming.net http://hkinsley.com https://twitter.com/sentdex http://sentdex.com http://seaofbtc.com |



 Searching...
Searching...

